Have you ever wondered about the different types of plastics and how they affect our planet? Understanding plastics is key to making informed choices and contributing to a cleaner, greener world.
Plastics are synthetic materials made from polymers, which are long chains of molecules that are found in nature or developed in laboratories. They are lightweight, durable and versatile, making them an essential part of daily life. From packaging to construction, plastics are everywhere.
Plastics have revolutionized industries by providing affordable alternatives to traditional materials like wood and metal. They help reduce the weight of cars, improve medical devices and even make their way into our homes in the form of appliances. Plastics also help to preserve trees and natural resources by replacing paper products and packaging.
While plastics offer numerous benefits, their environmental impact is significant. Plastics can take hundreds of years to decompose if they end up in landfills or oceans, which can harm wildlife and our planet. By recycling plastics instead, we can all make a difference.
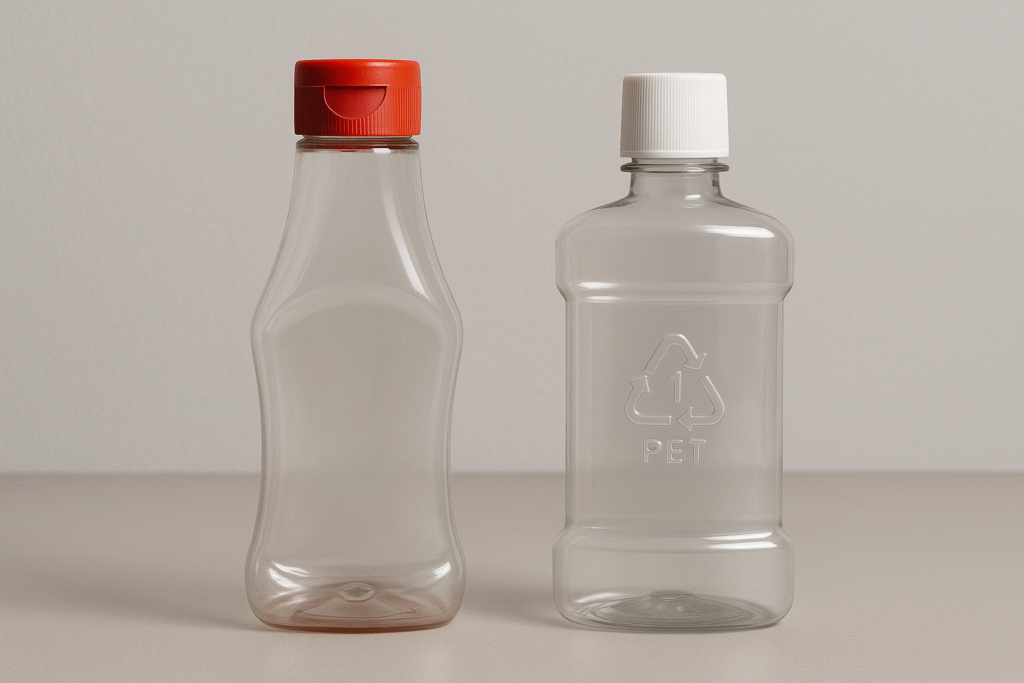
Accepted in recycling
Common uses of PET
PET is commonly used in beverage bottles and food containers. It’s lightweight and shatter-resistant, making it a popular choice for packaging.
Identifying PET
PET items are usually transparent and have a recycling symbol with the number 1. When crushed, they produce a loud crackling noise, distinguishing them from other plastics.
Recycling PET
In Canada, PET packaging and containers are accepted for recycling. Once recycled, it can be transformed into new bottles, clothing fibres and packaging materials. This makes it one of the most recycled plastics.

Accepted in recycling
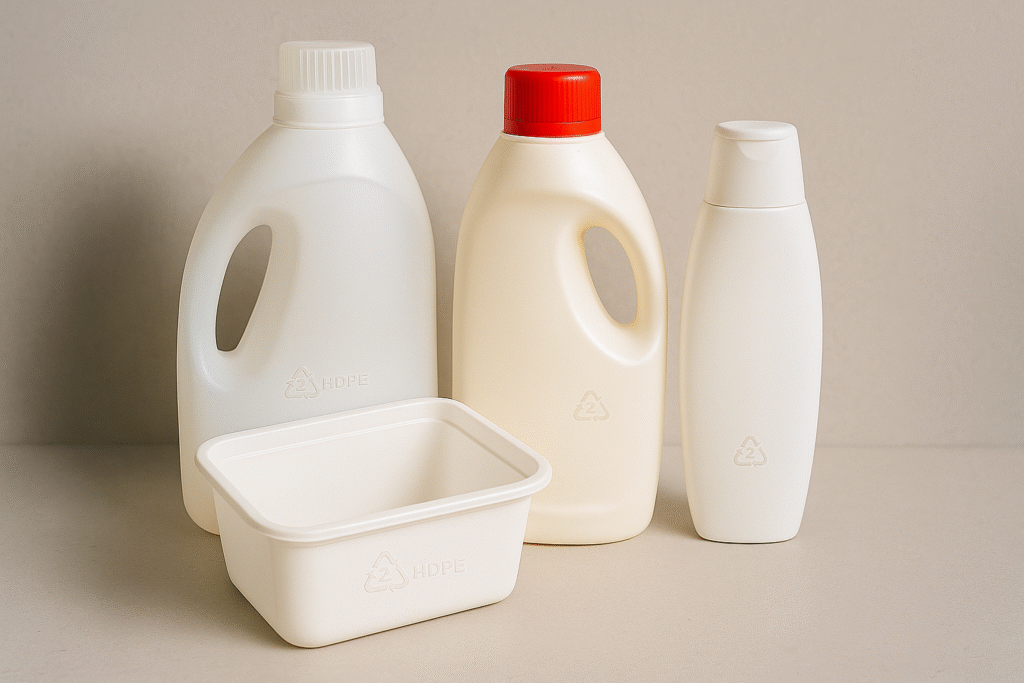
Common uses of HDPE
HDPE is known for its strength and is often used to make milk jugs, detergent bottles and plastic bags. Its durability makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Identifying HDPE
HDPE items are typically opaque and have a recycling symbol with the number 2. They are flexible and produce a soft crackling sound when crushed.
Recycling HDPE
HDPE containers are recyclable across Canada. Once recycled, HDPE can be turned into new containers, piping and even plastic lumber. Recycling HDPE helps keep materials used again and again while also conserving our planet’s natural resources.

Accepted in recycling
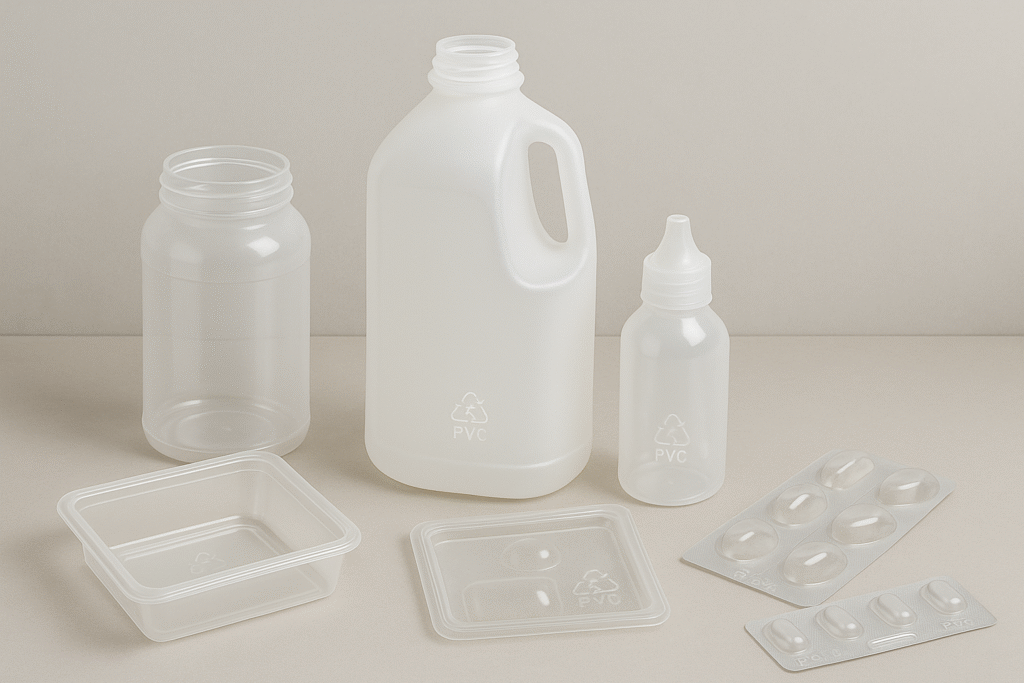
Common uses of PVC
PVC is a versatile plastic used in pipes, window frames and flooring as well as some jugs, jars and packaging. It’s known for its rigidity and resistance to chemicals.
Identifying PVC
PVC items may have a recycling symbol with the number 3. They are usually rigid and can be difficult to crush.
Recycling PVC
PVC packaging and containers are widely accepted in residential recycling programs across Canada. However, some PVC materials such as oil containers, garden hoses, inflatable pools and toys should not be placed in your recycling but rather dropped off at designated recycling centres or dontaed.. These include containers containing corrosive or hazardous materials.

Mostly accepted in recycling
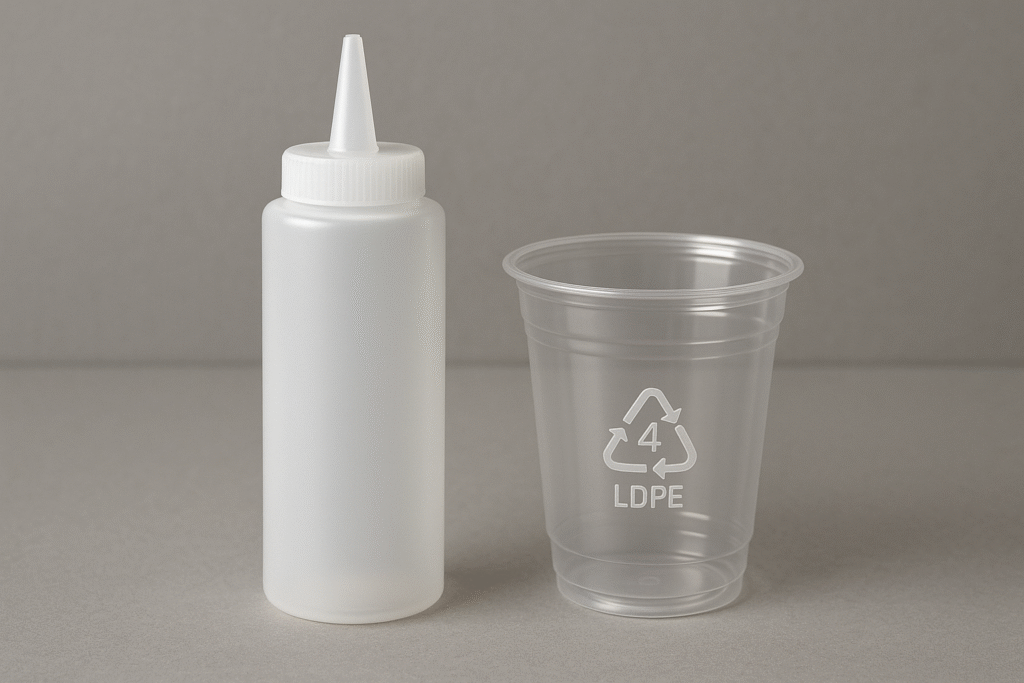
Common uses of LDPE
LDPE is used for making plastic bags, shrink wraps and squeezable bottles. It is flexible and has a high moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging.
Identifying LDPE
LDPE items have a recycling symbol with the number 4. They are soft and can be easily bent or crushed without making noise.
Recycling LDPE
While LDPE is recyclable, it is less commonly accepted in curbside recycling programs as the infrastructure to do so is not available everywhere today. Be sure to check your local recycling program to find out what is accepted.

Mostly accepted in recycling
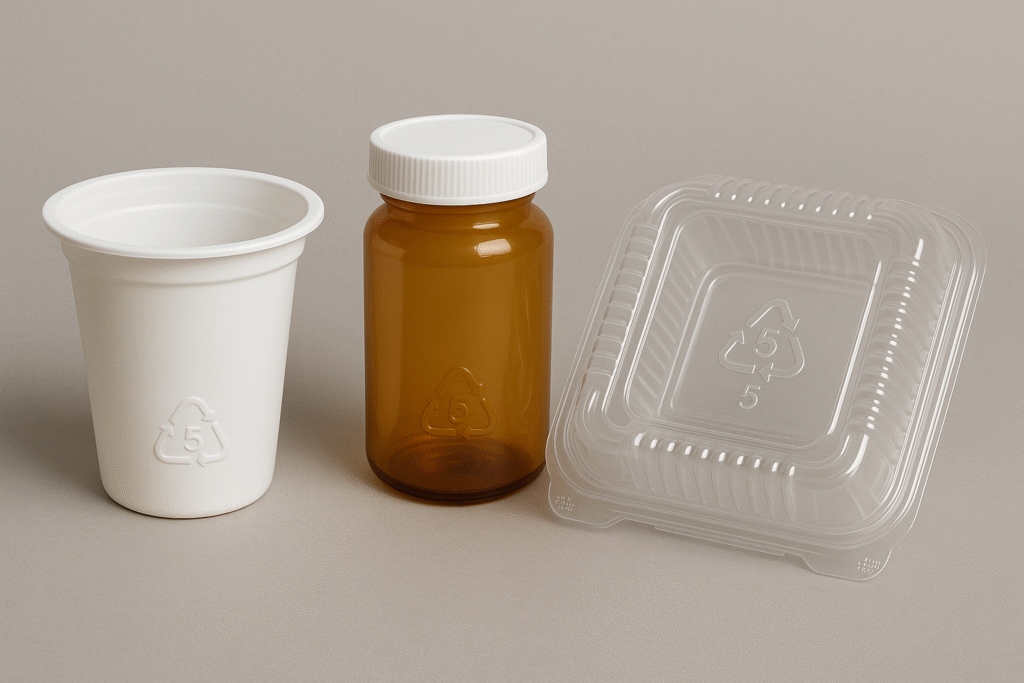
Common uses of PP
PP is used in yogurt containers, takeout food containers, cold drink cups, bottle caps and automotive parts. Its resistance to heat makes it suitable for products that require sterilization.
Identifying PP
PP items carry a recycling symbol with the number 5. They are often semi-rigid and produce a low-pitched sound when crushed.
Recycling PP
PP packaging and products are generally accepted in recycling programs across Canada. It can be processed into new containers, automotive parts and textiles, conserving natural resources.

Rigid PS is accepted in recycling
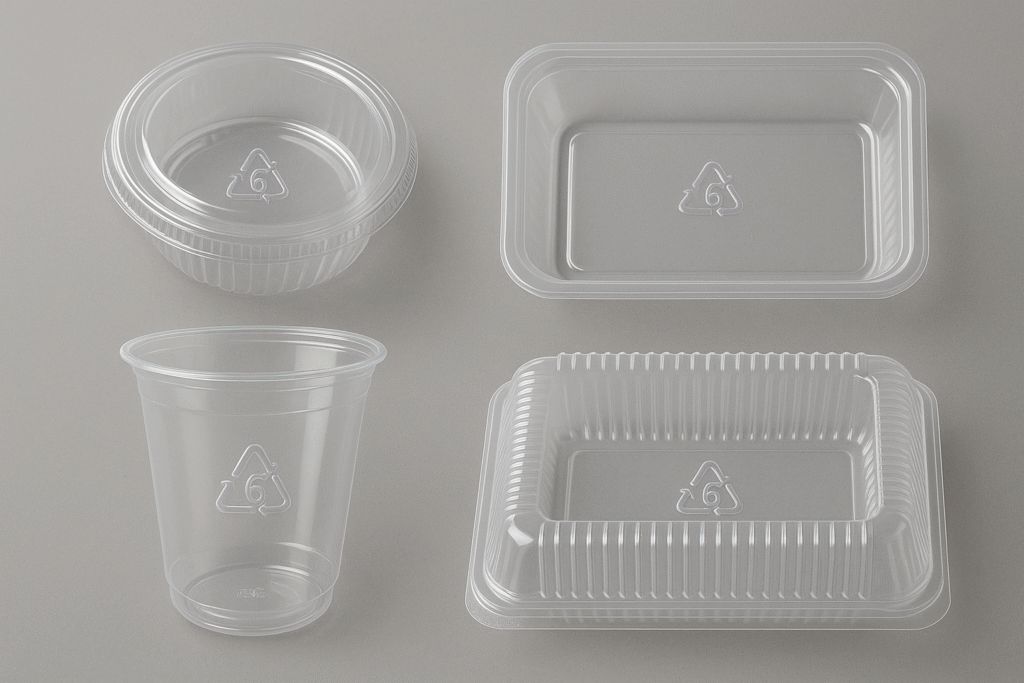
Common uses of PS
PS is used for disposable cutlery, clamshell packaging, foam and CD cases. It’s lightweight and has excellent insulation properties, making it popular in packaging.
Identifying PS
PS items have a recycling symbol with the number 6. They are brittle and produce a sharp sound when crushed. There are two general types of PS: Rigid and Expanded (i.e. styrofoam).
Recycling PS
Rigid PS packaging and products, for example clamshell containers are widely accepted across Canada. However, please check your local recycling guidelines to find out where you can recycle expanded polystyrene.
Make sure you give your containers a quick rinse before placing them in your recycling to avoid contamination.
No need to remove lids, caps or labels from containers. These can be recycled too!
Only recycle the types of plastics that are accepted in your local recycling program.

By understanding and identifying the different types of plastics and knowing how they can be recycled in Canada, you can contribute to a cleaner environment.
Your actions can make a difference in reducing plastic waste and preserving our planet for future generations.
Learn more about our partnerships and initiatives with plastic-focused organizations here.
Ready. Recycle. Repeat